The initial meeting
In the February of 1845 another advert appeared in the local press. This advert offered the speculator the chance to purchase shares in the new company. A prospectus was issued about a month later.

Of course, many of Hull’s townspeople had seen this stuff before some 5 years ago and were watchful of developments. The Hull Packet of the 7th March simply said that, ‘We hear that a great number of shares have been taken to forward the project of a new cemetery at Hull, and that the provisional committee consists of some of the more influential inhabitants of the town.’
The press were quite right. Some of the most influential people of Hull were involved. What the press did not know was that a meeting had taken place on the 5th March. This meeting took place at the offices of Charles Spilman Todd at 15, Bowlalley Lane. Below is a picture of that address today. It is now a private house.
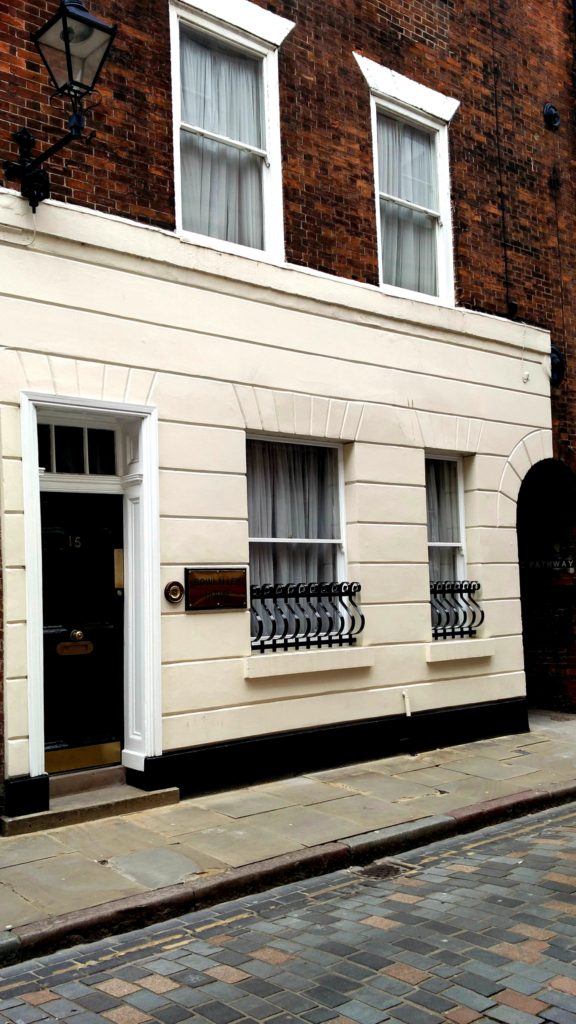

Charles S.Todd was to become both Sherriff of Hull and also the Town Clerk. At this time he was merely a practising solicitor and the solicitor for the proposed cemetery. It is from this date that the creation of the Hull General Cemetery really begins.

The Committee
Throughout March and April, the local press continued to run constant adverts for people to buy shares in the new company. The names behind the Committee were now published and the bankers too as part of these adverts.

By the 12th March the draft of the Prospectus was examined by the Committee and on the 19th it was released to the press. By the 5th April C.S.Todd could tell the Committee that he had received 400 share applications. It looked like the time was right for the creation of the Cemetery and its success.

You may notice that the membership of the Provisional Committee had increased. Whilst some early adherents had left, such as Edward Brady, this was more than compensated by the new arrivals. Sir William Lowthorp had joined the committee. He had been the mayor of Hull in 1837. It fell to him to present the town’s best wishes to the newly installed monarch. As a result he was knighted. He was also the father-in-law of Dr. Gordon. William Watson was another landowner to the west of Hull who had joined the committee.
John Solomon Thompson
The most important new arrival, however, was John Solomon Thompson. This man was to become the first chairman of the Cemetery Company, and in some ways, the best. He guided the Company through its initial days of purchasing the land and laying it out. His negotiations with the London and Midland Railway Company when their proposed rail line would have demolished the front of the Cemetery were admirable. He was also instrumental in pursuing the Act of Parliament that incorporated the cemetery. This in the face of the Hull Corporation pursuing its own Act of Parliament which would have enabled it to take over the cemetery. He will be the subject of an article later this year.
Evidence of something more substantial than simply selling shares was indicated by an advert in April that appeared in the press showing that the new company directors were not being idle and were actively seeking a suitable site for the Cemetery as may be seen below.
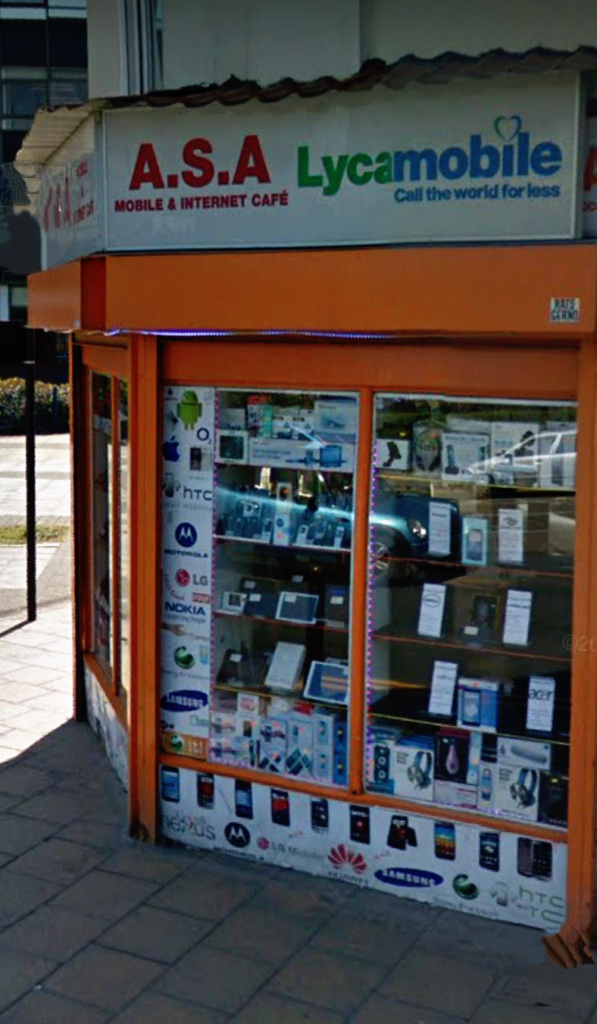


Above is no.15, Spring Bank today, which was the site of the temporary offices of the secretary of the Cemetery Committee, Shadrach Wride before the building of the Cemetery Lodge
Finding the perfect site
Some two days later C.S.Todd reported to the Committee that he had written to Mr Webster of Yafforth Grange. This gentleman owned property that was suitable for the cemetery. We’ll return to this person later.
By the end of April two more offers of land had been received. One plot was on Dansom Lane from the Revd. Nicholas Walton. This was dismissed out of hand. The Committee felt the price asked was ‘an exorbitant one and the offer could not be entertained.’
The second offer was for a site in the village of Marfleet, ‘A close of about 12 acres adjoining Marfleet Lane on the Holderness Road and belonging to Mr Pease’. This man was one of the bankers for the provisional Company. However, when C.S.Todd wrote to Mr Pease’s solicitor, Mr Saxelbye, who later was one of the first inhabitants of a large house overlooking Pearson Park, the offer of land was withdrawn.
Webster and Pearson
But by the time this offer was received and withdrawn, Mr Webster had replied and asked the Committee how much land they desired. As a result John S. Thompson and C.S.Todd set off on the long journey by coach to Northallerton. Instructed to ‘make the best bargain possible’ and not to offer more than £220 per acre their instructions were clear. Sadly, Mr Webster wanted £350 per acre and the deal fell through. Later, Zachariah Pearson bought the land it and became Pearson Park.
The map below is from1847. It shows what was to become Queen’s Road running along the top of the map from the top right hand corner till it joins Newland Tofts Lane, later Princes Avenue. The Sculcoates Union Workhouse, later Kingston General Hospital, can be seen at the right hand side of the map. The upper central portion is Webster’s land which became Pearson Park in 1860.
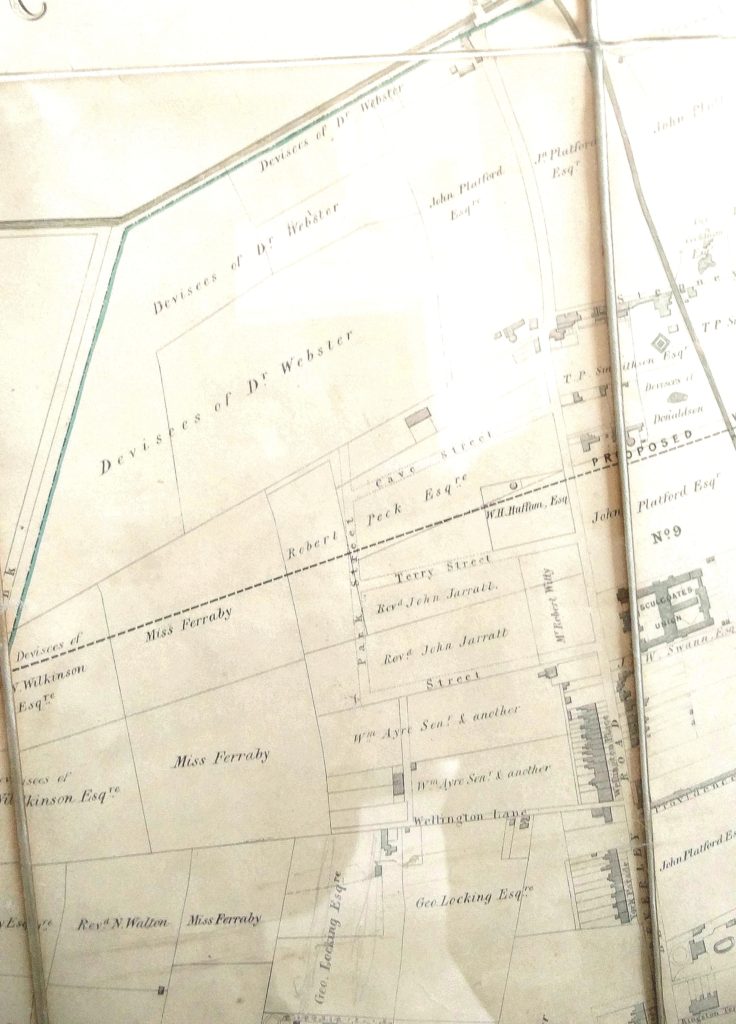
Enter Mr Broadley, M.P.
The Committee had another offer of land throughout this period. On the 5th May Charles Stewart had alerted the rest of the Committee to it. Henry Broadley had a site ‘on the Spring Bank of about 19 acres’.
Henry Broadley, and indeed the Broadley family, are well known. He was an M.P. for the County and it was said that one could travel across the East Riding without stepping off his land. Conservative in nature, and conscious of his position, he was a strange mix.
He owned tenements in Leadenhall Square that were so dire that the Corporation and the Church railed against them. Many of them were brothels or worse.
Foster, in Living and Dying, cites one instance where a policeman, entering one of these premises, disturbed a lady plying her trade with customers. In the ensuing struggle, the policeman’s presence caused a rotten window frame to be dislodged and broken. When this episode was reported in the press and debated in the Council Chamber the landlord was excoriated. Sir Henry, rather than be embarrassed, sued the Corporation for damage to his property.
Yet, he donated time and some money to helping young people away from crime. And he was very interested in treating the dead with dignity.
By the 28th May C.S.Todd was instructed to proceed with the necessary arrangements to buy Mr Broadley’s land. Of course nothing was that simple. Broadley instructed C.S.Todd to deal with his land agent. His land agent said he did not have the leeway to deal with the Committee. Broadley then said that he could not contemplate any discussion about the land until Parliament went into recess. As such the Committee were left in limbo.
The drainage report and public disquiet
A report as to the drainage of this site, and of Dr Webster’s, was drawn up Mr Francis Tadman. He informed the Committee that the drainage of the Spring Bank site was about 4 feet 6 inches whilst the drainage from Dr Webster’s site was only 3 feet. This report finalised the Committee’s determination to acquire the site.
However, to the general public, things had gone suspiciously quiet once again, as this letter to the Hull Packet showed.

The first AGM
The following month the Committee, probably reacting to this pressure, felt they should inform their subscribers of the situation. They called a General Meeting of the subscribers for the 29th October. The Chair, J.S.Thompson, outlined what the Committee had attempted to achieve. He then set out the difficulties they had met in acquiring a site. Finally, he outlined both of the sites points. Below is the record from the meeting related to the Spring Bank site.

As you can probably guess, the Committee recommended to the subscribers the purchase of the site on Spring Bank. Henry Broadley offered the site on Spring Bank for £300 an acre. This land was to be the site of the creation of the Hull General Cemetery.
The formation of the Company
At this same AGM the Committee felt that a resolution should be put forward to form the Hull General Cemetery Company. Needless to say, the resolution to buy the Spring Bank site, ‘at such price and upon such terms as they deem advisable’ was passed. As was the resolution to form the Company.
On the 31st October this news from the AGM was reported in the press. The news was what many people had been hoping to hear. It was reported that the Committee had held an introductory shareholder’s meeting to lay before them the progress they had made and that they desired the power from the shareholders, ‘for the purchase of Mr Broadley’s ground near the old Waterworks on the Spring Bank.’
This power was given to them under the resolution, ‘That the Company be formed and that immediate steps be taken for securing the purchase of a very suitable site near the Old Waterworks, offered to the Provisional Committee by Henry Broadley, Esq, M.P.’
General means general
The newspaper item went on to state that all denominations were to be allowed burial on the site. No doubt a view to both enhancing good will and maximising profit. Stating this was ensuring no shortage of future customers due to any short sightedness in terms of religious observances. In essence, the directors were adhering to the principles of a General Cemetery.
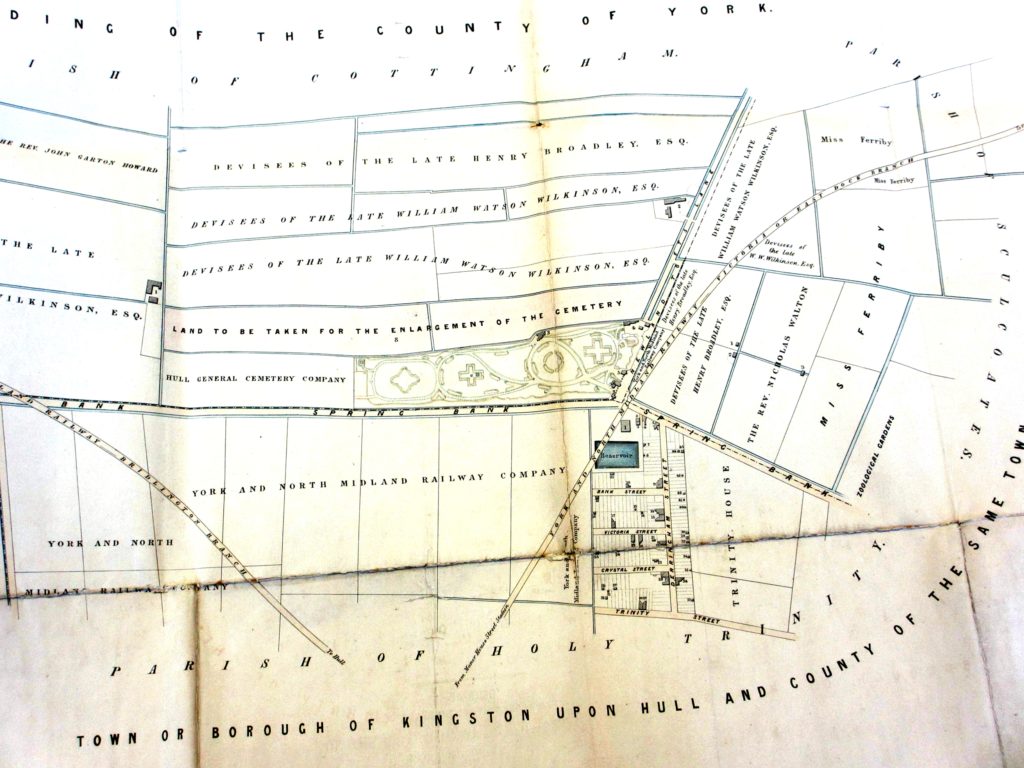
The map above was drawn in 1854 for the Hull General Cemetery Act. As you can see the proposed enlargement of the cemetery would have taken it to what would become Chanterlands Avenue. It would have engulfed the future sites of both Newstead and Welbeck Streets. An article on how this proposed plan to enlarge the Cemetery will be published later this year.
The map shows both the reservoir at what was the end of Bank Street, now entirely subsumed under William Jackson’s’ factories, and also the beginnings of Princes Avenue but known then as Newland Tofts Lane. The cemetery was in the parish of Cottingham and was well out in the country and therefore met the criteria as laid down by the 1843 statute mentioned in the previous part of this article.
A grand boulevard
Tying neatly with other civic aspirations as to a grand boulevard or promenade being developed, the Committee also stated that if they took up the option to buy Mr Broadley’s land they would also seek help and apply for a grant from the government, “for making a Promenade on the Spring Bank, as had already been proposed.”
This proposal stemmed more from the proprietors of the Zoological Gardens than it did the Hull General Cemetery Company as the zoo attempted to encourage more business for their venture. Indeed, although this isn’t clear from the documents, I believe it was the Zoological Gardens that made the appeal for the grant. The idea for a “promenade” along the Spring Ditch had been mooted in 1830 by Charles Frost and associates but had never been acted upon due to financial issues.
Cheap is best!
Civic pride being what it is, and the Victorians being the way they were, an article in the Hull Packet of the 21st of November positively crowed that Hull had not only spent less on procuring a cemetery than other significant towns in the country but that it was bigger than those others too. This before the site was actually bought and well before a body was buried there!

The structure of the Company
On the 17th November, the bare bones of the Company and how it would work was laid out to the subscribers and passed unanimously. The voting at AGMs would be determined on how many shares a subscriber held. No one could have more than five votes no matter how many shares they held. There would be seven directors and no one with less than five shares could become one. The first directors were as follows: William Irving junior, John S Thompson, George Milner, Benjamin A.Tapp, John Malam, Charles Stewart and John Robinson.
Auditors would have to hold three shares at least. These first auditors were Thomas Abbey and Thomas Dalton Hammond. The bankers, Pease and Liddell, were chosen and the directors and auditor’s remuneration for their work was accepted.
Two further resolutions
Two further resolutions were passed at this meeting. Both would be problematic for the Company in later years. The first effectively restricted it’s capital to £10,000. A goodly sum in the ‘hungry 1840s’ but this would prove not be enough to finance their enlargement plans a decade later. To do that they would need to issue a further tranche of ‘half-shares’. Just another further complication.
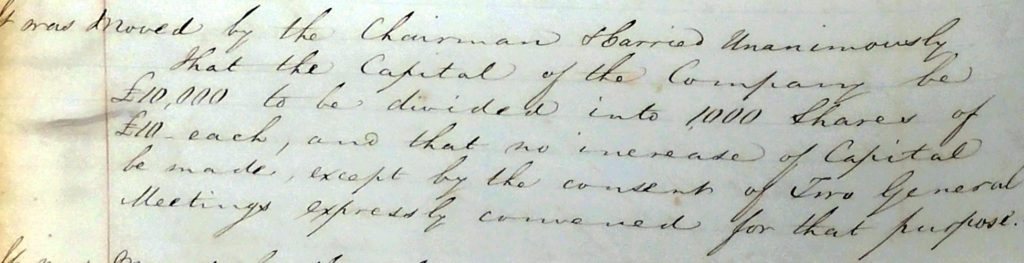
The second resolution would prove more disastrous.

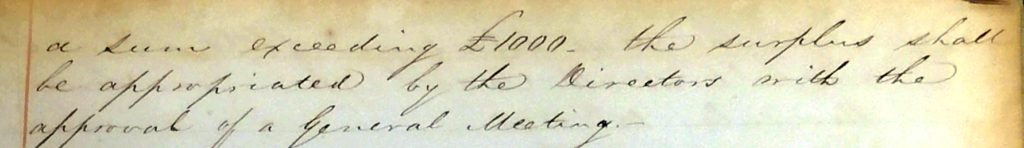
On the face of it an eminently sensible action. To create a Reserve Fund from the annual profits was sound business principles. If it had been used like this, for example, ‘extending operations of the company’ the Cemetery could even now be a going concern. Where it failed was in the first point of the Reserve Fund. ‘For equalising Dividends’.
This was fine during the good times but this Reserve Fund was used throughout most of the Cemetery’s life in the 20th century to prop up the dividends to the shareholders. But by then it was surrounded and could not expand anyway. It had frittered away its life blood keeping its dividends at inflated levels and failed to plan long term. And it was this resolution, made in November 1845, that allowed that to happen.
This is the second part of the story of the creation of Hull General Cemetery. The third part will appear next month.

Pete Lowden is a member of the Friends of Hull General Cemetery committee which is committed to reclaiming the cemetery and returning it back to a community resource.

