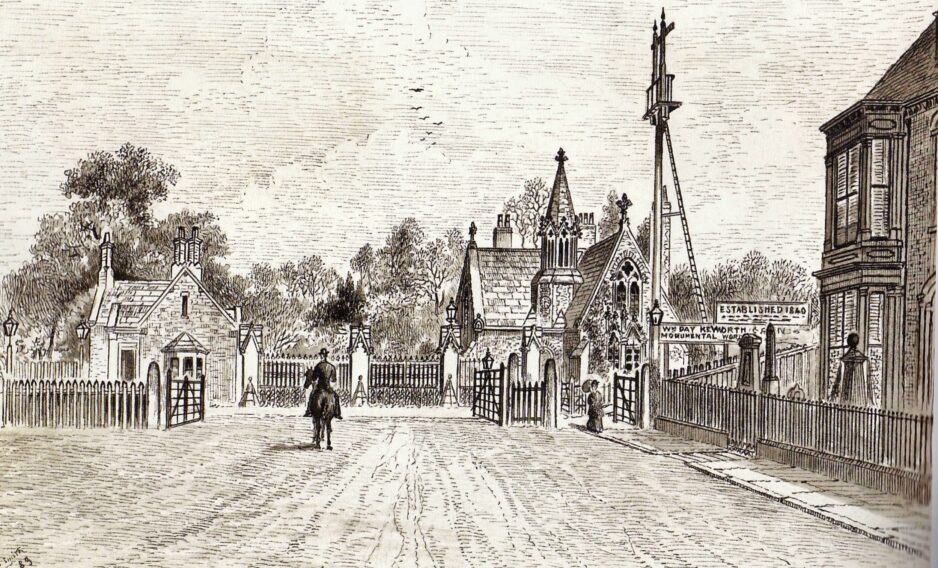
The Beginnings of Western Cemetery
Western Cemetery is a large cemetery situated about a mile and half from the city centre of Hull. It comprises of approximately 37 acres and it is unusual for it is divided by a main road, Chanterlands Avenue. People walking around it, sometimes with dogs, in summer with children, treat it as a public space complete with headstones. Although there are still funerals in there, these are quite a rarity these days. There are no services held there now as the Cemetery no longer boasts any chapels. In fact, it is a pleasant ‘country’ walk. Which is a far cry from its beginnings. This article is a short history of this place of rest for many of the town’s residents.
The beginnings of Western Cemetery, or as it was originally called, the Borough Cemetery, are closely tied up with its next-door neighbour, Hull General Cemetery.
Hull General Cemetery opened in 1847. The owners purchasing 18 acres from Henry Broadley M.P. By 1854 it had developed about 10 acres for burial. By the 1850s it would sign separate covenants with both the Society of Friends, also known as the Quakers, and the Hull Workhouse Board that would swallow up another 3 acres. This left 5 acres at the extreme westernmost point of the Hull General Cemetery undeveloped. These were still let out as allotment gardens.
Politics: Local and National
At this point it would be helpful to touch upon both the national and local politics of that period. For both would have an effect upon the creation of Western Cemetery.
In 1848 the Liberal Government of Lord John Russell enacted some legislation. This was probably the first crack in the wall of laissez-faire values. This was the first Public Health Act. It was radical in that it not only took on the role of public guardian of the health of the nation but could be seen to infringe upon private interests such as water companies and private cemeteries. It also empowered local authorities to develop and enact local initiatives to make the health of their charges better, be that via housing, sanitation reform, medical provision etc. Not least of these was the creation of local burial boards. They would oversee the maintenance, provision and delivery of the burials within their jurisdiction.
Cholera and the Local Board of Health
With this legislation in force the Hull Corporation began its work to improve the health of its citizens. Almost before it could get into its stride Hull, and indeed the whole country, suffered from the effects of the second pandemic of cholera. This disease, waterborne by the cholera vibrio bacillus, struck Hull badly. During a four-month period the town lost 3% of its population. This was probably the most destructive visitation of a disease in Hull since the Black Death stalked the land. The Local Board of Health (LBOH) could do nothing to mitigate this disaster. An attempt to clean afflicted housing and whitewash the internal walls was the sum total of the Board’s efforts.
There must be some degree of sympathy for the Board’s efforts. No one knew then of the existence of things like bacillus. How disease could be transmitted by such miniscule creatures was more of a mystery. In fact, the prevalent view amongst the public, and indeed medical practitioners, was that disease was caused by bad smells. This idea of how diseases were transmitted goes back to the time of Aristotle and Galen. This thinking had little changed by the early 19th century. The term ‘mal air’ or bad air can be seen to be the root of the term ‘malaria’ which is an example of that kind of thinking.
Suffice to say that preventative measures to reduce or alleviate the effects of the cholera were ineffective. The LBOH and the inhabitants of the town simply had to wait for the disease to run its course. By October deaths began to fall and by the following month no more deaths from cholera were recorded. The Board now could begin its work in earnest.
The Race for Legislation
One of the first things it looked at was purchasing the Hull General Cemetery. The offer for it was rejected. The LBOH then began to look towards legislation via parliament to gain control of this cemetery. By 1854 it was seeking, via the Kingston Upon Hull Improvement Act (1854) to compulsory purchase the cemetery. Similarly, the Hull General Cemetery Company looked to its own legislation to protect itself from this scheme. It sought to have the Cemetery Company incorporated. This would protect it from any form of compulsory purchase. The race was on. The Hull General Cemetery Company won that race, probably because their bill was much simpler that the Hull Corporation one. This Bill was looking at many other factors than simply burials and the disposal of the dead.
To Buy or Not to Buy
A part of that Hull General Cemetery Company Act was the clause that allowed the Cemetery Company to compulsory purchase the adjacent land to the North. This area, now comprising of Welbeck, Thorseby and part of Newstead Streets, was owned by the Wilkinson family of Cottingham. The Cemetery Company had unfortunately fallen foul of this family when a mix up over what the Company thought was a verbal agreement saw its workmen entering Mr Wilkinson’s grounds and felling his orchard trees. Legal threats ensued and the relationship between the two had remained frosty even after Mr Wilkinson died.
Problems over the valuation of this land and the intransigence of the Wilkinson family suggested that the only recourse the Company had was to pay for, and attend a Sheriff’s Court, who would adjudicate this valuation. The Company, short-sightedly, decided that the expense could not be justified and the matter was left in abeyance.
By 1855 Hull General Cemetery was not only protected from the threat of being compulsorily purchased by Hull Corporation but was now in the ascendance. And here we need to just look back slightly to yet another piece of legislation arising from the 1848 Public Health Act.
No Dignity for the Dead
The state of the burial grounds throughout the country had long been a source of disquiet. Many of them were full yet still being used. In Hull the burial ground of St Mary’s in Lowgate was between 5 and 8 feet above the pavement. It was common knowledge that burials could only take place if the most recent coffins in that grave space were removed to accommodate the next burial. After some shocking stories of the mistreatment of the dead were recorded in the popular press and also by a public- spirited reformer called George Walker in his book, ‘Gathering from the Graveyards’ reform was demanded by the public. This took the form of the Metropolis Act of 1850.
This Act closed many of the disgusting and over-used burial places within the metropolitan area of London. The Act was then systematically rolled out throughout the country. By 1855 it was Hull’s turn. In Hull, both Holy Trinity and St Mary’s churchyards were closed, Also Trippett Street churchyard, which was the overflow burial ground of St Mary’s, was closed. St Peter’s in Drypool also suffered the same as did St Mary’s, Sculcoates. The Quaker burial ground in Hodgson Street was closed and the Jewish burial ground on Hessle Road was also shut. Castle Street survived as a burial ground on a technicality but was ordered to be shut by 1860.
Suddenly, almost overnight, Hull General Cemetery held a near monopoly upon burials in the area. This change in fortunes made the Cemetery Company even more resistant to being taken over by the LBOH. As such the LBOH changed tack.
Lease or Buy?
In the June of 1855 the LBOH again approached the Cemetery Company. Their new approach was that it could buy or lease the cemetery. If not that then perhaps it could buy or lease the 5 acres towards the west. The Company had not yet developed this area yet. The aim of the LBOH was to start a Borough Burial Ground. Over a period of two years the parties engaged in negotiations. It wasn’t until the AGM of the Cemetery Company in March 1859 that the board of directors stated that,
The negotiations with the LBOH are all but concluded and your board now think this the proper time to lay the arrangement before you. The deeds to carry out the arrangement with the local board are already prepared and require sealing to complete the matter. On the completion of the arrangement with the LBOH your directors propose to call a special meeting of shareholders as the funds for building a new chapel (required under any circumstances.) and for fencing, planting, draining and laying out the portion of ground set apart for the LBOH will then have to be voted on.
By the July of that year agreements had been signed for the drainage and fencing of the five acres. In the September the contact for the erection of the new chapel was signed and later that month the site was chosen and on the 3rd October the foundation stone was laid by the Mayor, Marin Samuelson, of Sammy’s point fame. This chapel was demolished in the 1920s.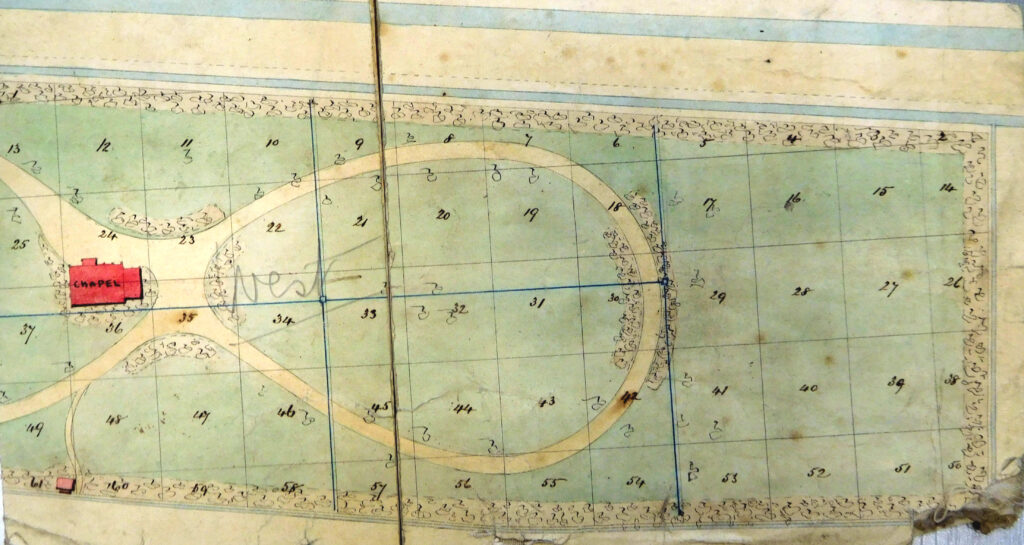
This is a map of the five acres originally leased by Hull Corporation in 1859. The future Spring Bank West is to the top of the map and the Hull General Cemetery is to the left.
No Division in Heaven
The five acres were leased to the LBOH for the period of 500 years. One final hiccough appeared via the archbishop who demanded that the new chapel could only be used for Anglican burials and that the old chapel in the grounds of Hull General Cemetery should be used for Dissenters. Both the LBOH and the Company agreed to this unreasonable demand and the ground was consecrated accordingly. Later this stipulation would entail the building of another chapel to cater for Dissenters when the LBOH and the Company fell out with each other.
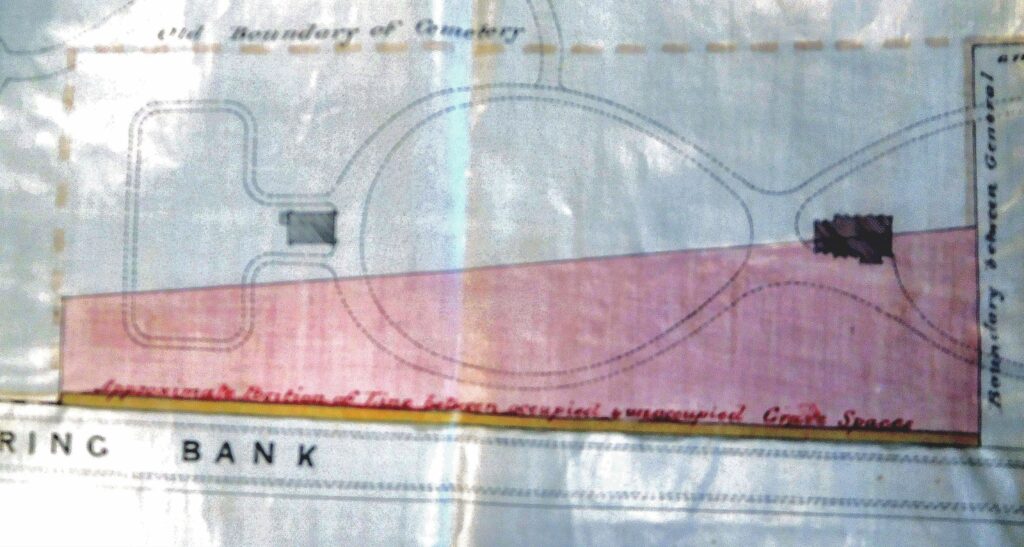
Map of the original five acres showing the consecrated area in pink and the unconsecrated and other religion’s burial area.
At this time, we have the Hull General Cemetery Company operating its own concern. It was also conducting the burials and maintenance of the Hull Corporation’s new burial ground. This arrangement lasted less than two years.
A Moment of Madness?
In June 1861 the chairman of the Cemetery Company informed his fellow board members that he had sent a letter to the LBOH. This letter was sent as a result of him being present in the council chamber at the time of a debate upon burial fees. In this debate, which centred upon the plan by the Holy Trinity Church to develop some three acres they had been given to them by Sophia Broadley as a burial ground for the parish to compensate for the closure of Castle Street, the high cost of burial in Hull General Cemetery was raised and commented upon unfavourably.
The Fateful Letter
The chairman, William Irving, being also a councillor, was angered by the tone of this debate, as he thought, this discourtesy to the Cemetery Company was unjust after all they had done to accommodate the Hull Corporation with the new burial ground. As such he penned the following letter,
To the Burial Committee, LBOH 8/5/1861
Gentlemen, I have read with surprise the report of your board meeting on the 29th Ult and the resolution passed on the occasion. It appears to me that your board in dealing with the burial question have not fairly considered the rights of the Cemetery Company.
At the request of your board the company entered into an arrangement to provide 5 acres of land, then let off as gardens, as and for the place of burial for the inhabitants of the borough; to lay out the same as an ornamental cemetery and also to erect a suitable chapel thereon; and when the ground should be found insufficient the cemetery engaged to provide another suitable and adjoining piece of land and set it apart in the same way for your board.
These works have been carried out by the company at a cost of £1328 exclusive of land.
The Letter went on…
The company have justified their part in this agreement to the letter, and also to the satisfaction of your board as the following resolution of the 5/5 1860 will prove.
The company, in expending their money to meet the requirements of the board naturally looked to a fair return in the shape of interest on the outlay but your board’s resolution of the 29th ult renders it hopeless. The company think that in arriving at such a decision your board were wholly regardless of the position of the company with your board under the arrangement referred to the effect of your resolution being to deprive this company of the whole or a large part of their anticipation.
Under these circumstances. I have to suggest whether the proper course for the LBOH to adopt would be to purchase the ground included in the arrangement and thus, by taking the whole affair into their hands, release the cemetery company from their present unsatisfactory position, brought about as it has been by the action of your board.
Should the above suggestion to purchase meet with your views and should your board decide on adopting it, you would then be in a position to provide a family burial place in the board’s cemetery for the fees alone, which you can regulate at your pleasure and thus preserve the management of burials under your own control.
The Mistake and in Writing Too.
To carry out the suggestion the cemetery company would be willing to sell your board the land included in the arrangement on the following terms, subject to such regulations for preserving unity of design and uniformity of appearance as might be mutually agreed upon.
Say 5 acres of land at £315 per acre (the cost to the company £1575. Amount expended by the company in laying out, draining, planting and erecting a new chapel to meet the requirements of the burial board £1328. Total £2903.
The company would grant a perpetual right of road through the present cemetery, the board contributing their proportion of maintaining it in good order.
The Justification
The company think that they are fully justified in laying their suggestion before your committee, satisfied that they are entitled to their due consideration at the hands of your board for the large (and as far as they, the company are concerned, unnecessary) outlay they have incurred for the convenience of your board, and they would urge upon the board, through your committee, the necessity under existing circumstances. If your board’s arranging either to purchase the ground as suggested, or to give such compensation as may be mutually agreed upon.
In conclusion I may state that the object of the promoters of the cemetery company was to provide for the inhabitants of Hull what so much needed by them, a place of burial for all sects and denominations; to secure to all classes of the community the means of decent and undisturbed sepulture according to the rights of their own religious faith, and to put an end to intramural interments. This has been the aim of the company from its foundation to the present time and it was with this view, and not with the expectation of pecuniary gain that the arrangement with your board was entered into.
Yours
Wm Irving
Chairman, HGCC.
The Fallout from It
One wonders what his fellow directors thought of this letter, and of him sending it without asking for their approval. In an instant William Irving had curtailed any further development of the Hull General Cemetery. Its demise was certified by the LBOH’s response. In short, they accepted the terms in the Chairman’s letter. From the April of 1862, the Borough Burial Ground was independent of the Cemetery Company. That is except for the administration and the working and maintenance of the ground. This arrangement was continued for a sum of £180 per annum.
However, although the Cemetery Company did not realise this, the agreement was to continue only until the Borough could gain enough experience and employ its own labour force to take care of its own burial ground. The Cemetery Company received in final settlement the sum of £2903. This appears to be a small sum for committing suicide.
The Borough Burial ground was the genesis of the Western Cemetery. In 1864 it erected a new chapel to accommodate the Dissenters. This chapel was finally demolished in 1994. It had long been disused for services. It was used for the storage of plant and tools towards the end of its life.
The End of the Agreement
The Borough cemetery continued to cater for the Hull citizens whilst being managed by the Hull General Cemetery Company. However, on the 1st June 1880, the Cemetery Company received a rude shock. This was a letter from the Town Clerk and secretary to the LBOH, Charles Spilman Todd, later to become the Sheriff of Hull, stating that they were giving the Cemetery Company one month’s notice of the termination of the agreement that allowed the Cemetery Company to maintain and administer the Borough ground. A further letter that day said that the Hull Corporation were willing to enter into a similar agreement for a lesser sum of money.
Negotiations began in earnest once again between these two adversaries. By the August the Cemetery Company had grudgingly accepted the Corporation’s final offer of £130. This also included £5 for the upkeep of the connecting road. This was a reduction from the £180 and £20 which had originally been agreed back in 1862.
Such changes as this showed that far from being the major player in the burial business the Cemetery Company was now subservient to the Hull Corporation. One of the factors at play here was the recent opening of the Hedon Road Cemetery in 1878. A privately owned cemetery was beginning to look like an anachronism.
Expansion: Go West Young Man
The next change to Western Cemetery, newly named as such with the opening of Hedon Road Cemetery to the east of the city, was a huge expansion. From 5 acres to 37 acres, the new cemetery dwarfed its parent. The irony here was that this land to be purchased was from the Wilkinson family. In selling it to the Hull Corporation, they were exacting revenge for the decimation of an orchard 40 years ago. The only stipulation the Wilkinson family made was an access road should be made by the Corporation so that the Wilkinson land beyond the parcel being sold could be accessed by their tenants. This the Hull Corporation agreed to and the result today is Chanterlands Avenue.

The expansion of Western Cemetery in 1889 showing the beginning of Chanterlands Avenue.
This expansion took place in 1889. As part of that expansion was the creation of a new lodge for the superintendent, Mr Whitty. The building of a new Chapel on the western side of the new Chanterlands Avenue also took place. Another aspect of this expansion was that the Borough burials no longer needed to traverse the Cemetery Company’s grounds. They now had access to their own grounds from Chanterlands Avenue.
The Major Cemetery for Hull
Western Cemetery was the major cemetery in Hull at this time. Its heyday was perhaps the period from 1890 to the beginning of the second world war. After this time, it passed the mantle to Northern Cemetery, opened in 1916, and the Eastern Cemetery, opened in 1935.
It still continues to accommodate burials although there is now no longer any room for new graves. Such burials that take place are of family members being buried in family graves. In a few years’ time it will be in exactly the same position that Hull General Cemetery found itself in in the 1970s. The rise and fall of all cemeteries follow the same pattern. A short burst of growth at the beginning followed by a rapid expansion in its adolescence. A much longer period of maturity. This is followed by a period of decline merging into senescence at its end. Much like us all really.

Pete Lowden is a member of the Friends of Hull General Cemetery committee which is committed to reclaiming the cemetery and returning it back to a community resource.

